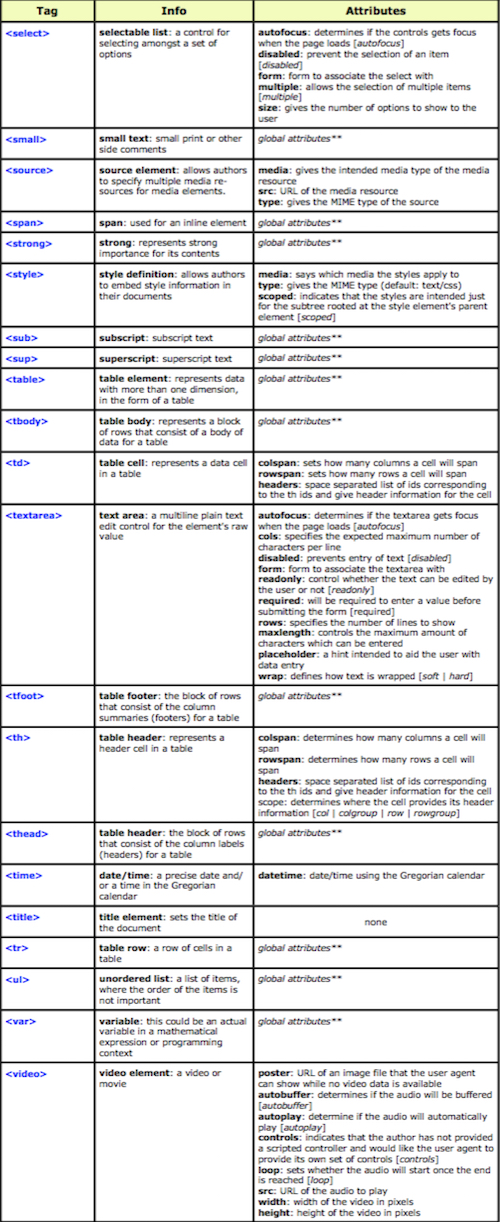
HTML5
HTML5 includes detailed processing models to encourage more interoperable implementations; it extends, improves and rationalizes the markup available for documents, and introduces markup and application programming interfaces (APIs) for complex web applications
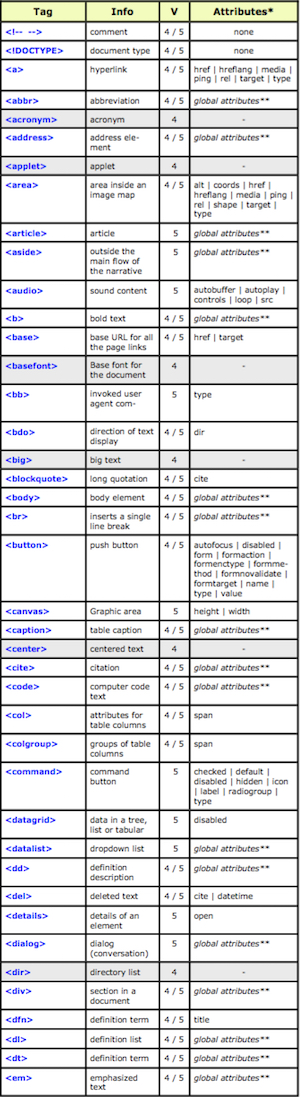
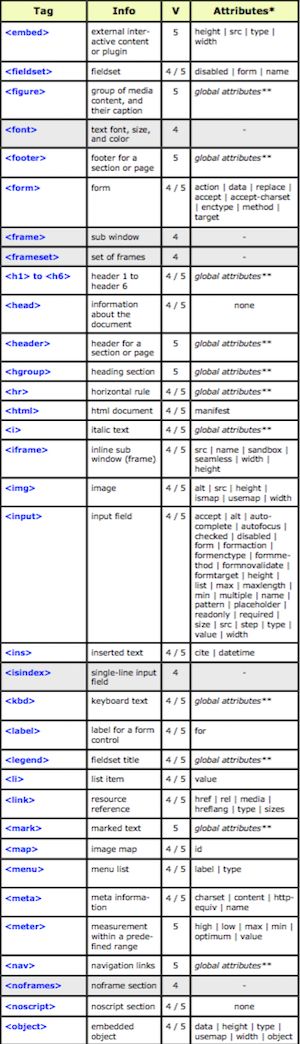
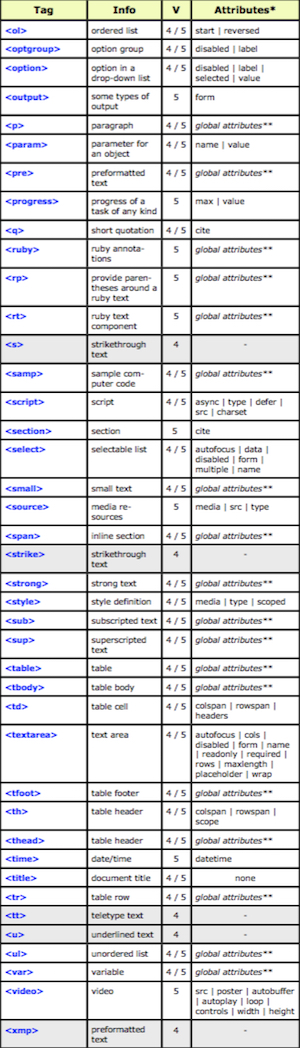
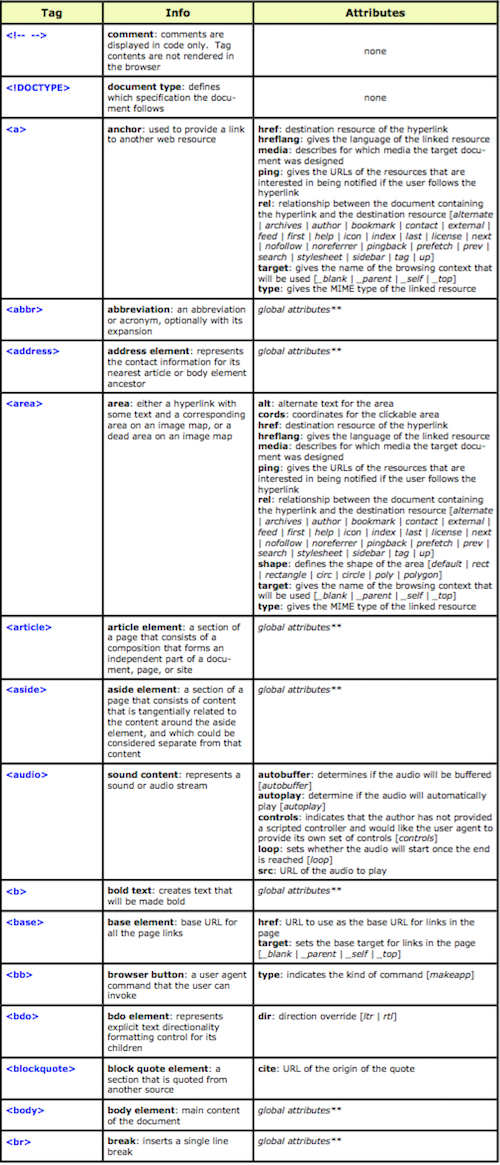
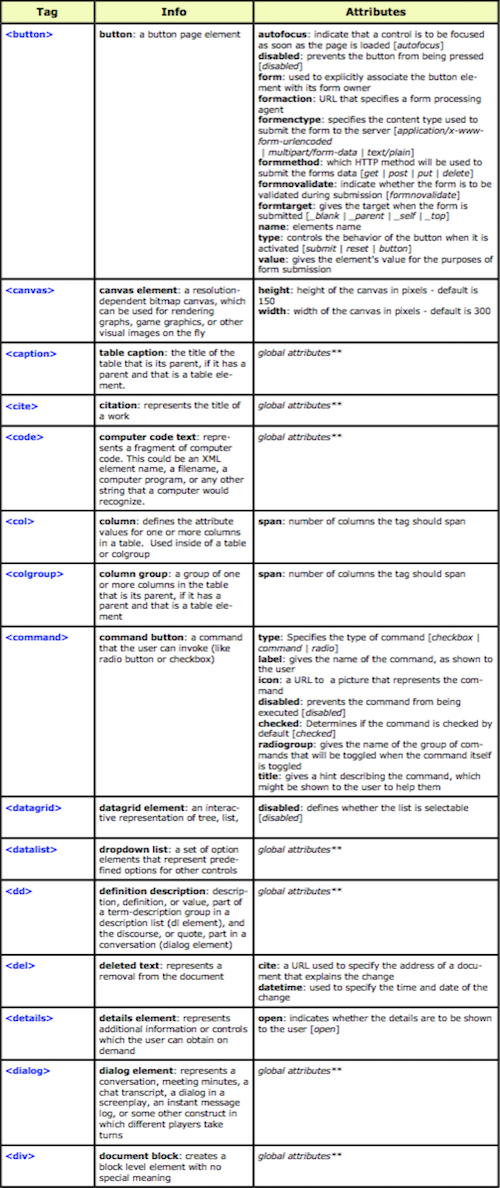
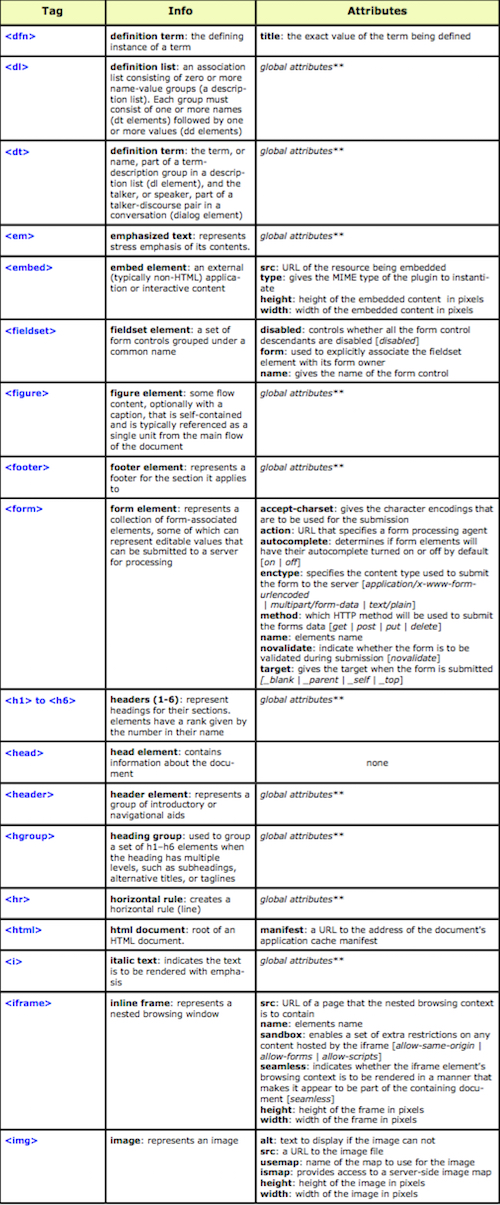
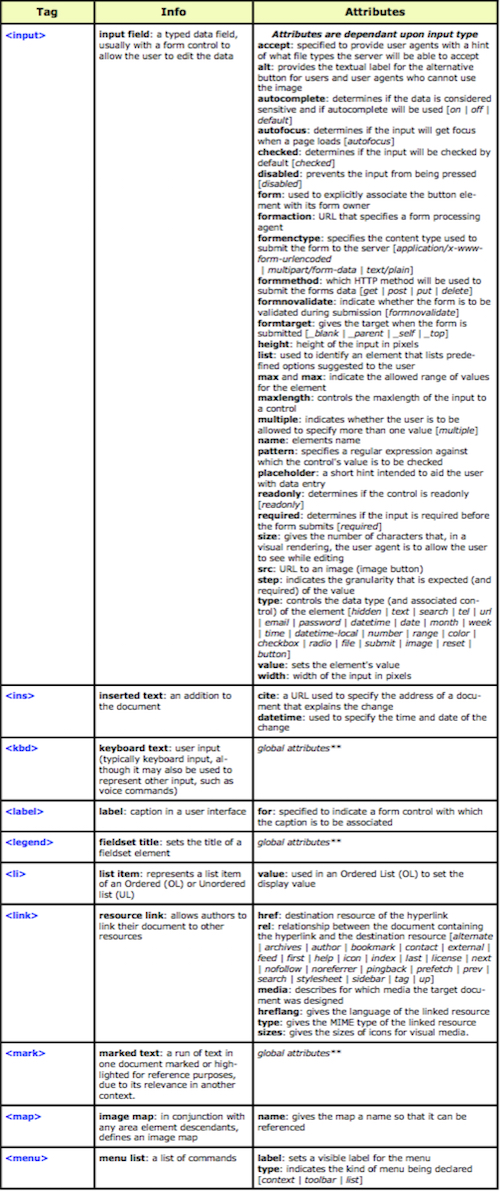
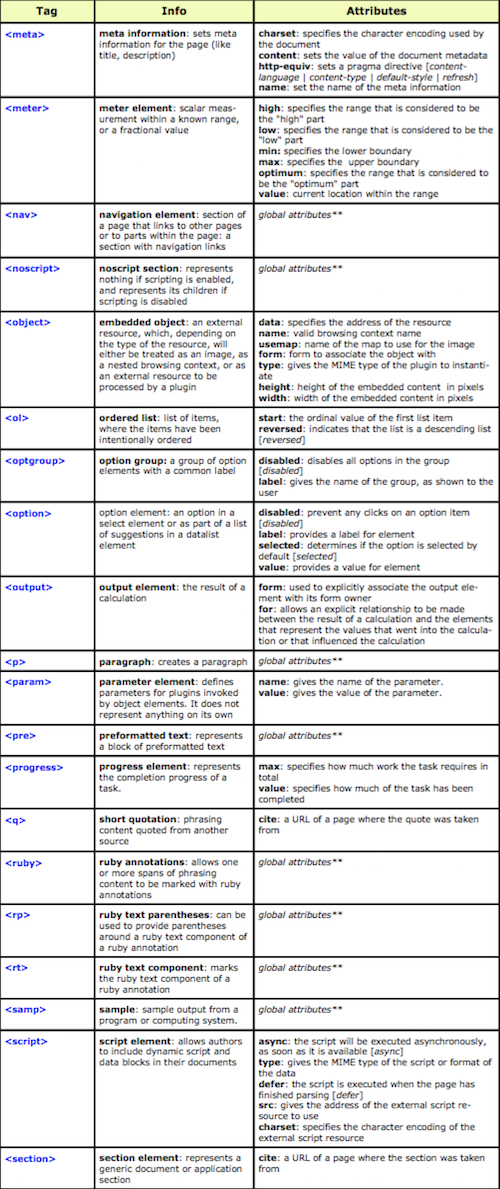
The “Hypertext Markup Language”, better known as HTML is a programming language which, as its name suggests, describes the format of your document content.
This standard provides a reference for the development of web pages in different versions, defining a basic structure and code (called HTML) for defining content of a web page, such as text, images, etc.
For example, it specifies the character and paragraph formats, images to be used, and so on.
WHAT IS HTML 5?
HTML 5 is the successor to HTML 4.
This latest version, should reflect the current needs and, therefore, includes some new features.
For example, allows internal playback video, audio and games. All without necessary further additional programs, such as Adobe Flash.
WHAT ARE THE ADVANTAGES?
HTML 5 gives developers new opportunities websites. Thus, web browsers as popular as Internet Explorer, Mozilla Firefox or Google Chrome already support HTML 5.
In addition, this standard also works well with smartphones and tablets.
Thus, it is possible to improve the speed and viewing web pages on mobile devices.
HTML 5 VS Flash
Flash consumes more resources, is unstable and reveals numerous vulnerabilities.
With HTML 5, any programmer can integrate the so-called “Rich Internet Application” (RIA) and include videos directly in the source code of the page. The browser can thus play videos, audio and even games.
For mobile devices this represents a great advantage.
Until HTML 5, Flash has been master of this sector but has little time left.